- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
- Least developed regions»
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Employment rate
- NEET
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Long term unemployment
- Unemployment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Slovakia – SK0
EU regions: Slovakia > Slovakia

| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 12.8 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 3.92 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 2.54 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 5.47 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 89.28 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 122.92 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2024 | 59.6 |
| NEET | 2024 | 8.7 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 74 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 72.4 |
More on wikipedia wikidata Q214 on OpenStreetMap Slovakia slovensky: SK0
Subregions: Bratislava Region, Western Slovakia, Central Slovakia, Eastern Slovakia

Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 5.4 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 19.2 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 3.5 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 64.9 |
| Unemployment according to labour offices | ||
| number of registered unemployed | October 2025 | 165 877 |
| number of unemployed women | October 2025 | 91 707 |
| number of long-term unemployed | October 2025 | 61 096 |
| number of vacancies | October 2025 | 116 571 |
Comparison of unemployment according to ILO methodology and registered unemployment yields some differences.

Data on unemployment in counties of Slovakia are available at Local Administrative Units data of Visegrad countries.

Demographics

| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2024 | 5 424 687 |
| population density | 2023 | 111.4 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2024 | 27.9 |

Employment by sectors, Slovakia
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 58.6 | 2% | B-E | 648.1 | 25% |
| F | 265.7 | 10% | G-I | 603.2 | 23% |
| J | 112.2 | 4% | K | 64.9 | 2% |
| L | 19.5 | 1% | M_N | 141.6 | 5% |
| O-Q | 626.2 | 24% | R-U | 79.6 | 3% |
| TOTAL | 2620.8 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].

From Wikipedia: Slovakia ( (listen); Slovak: Slovensko [ˈslɔʋɛnskɔ] (listen)), officially the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská republika, listen ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, and the second-largest city being Košice.
The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. In the 7th century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the 9th century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which would then become the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 and 1242, after the Mongol invasion of Europe, much of the territory was destroyed. The area was recovered largely thanks to Béla IV of Hungary, who also settled Germans, leading them to become an important ethnic group in the area, especially in what are today parts of central and eastern Slovakia.
After World War I, and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the state of Czechoslovakia was established.
Neighbours: East Austria, Central Hungary, Czech Republic, Great Plain and North, MAKROREGION POŁUDNIOWY, East Macroregion, Transdanubia
Subregions: Bratislava Region, Western Slovakia, Central Slovakia, Eastern Slovakia
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Regions of Slovakia - Slovakia – SK0, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/en/projects/eu-regions/SK0
Local Administrative Units data of Visegrad countries
Statistical data on LAU1 regions of Slovakia, Czechia, Poland, Hungary. This LAU1 panel data dataset on 556 regions contains data on population, age structure of inhabitants, on number and structure of unemployed and is regularly updated.. . .
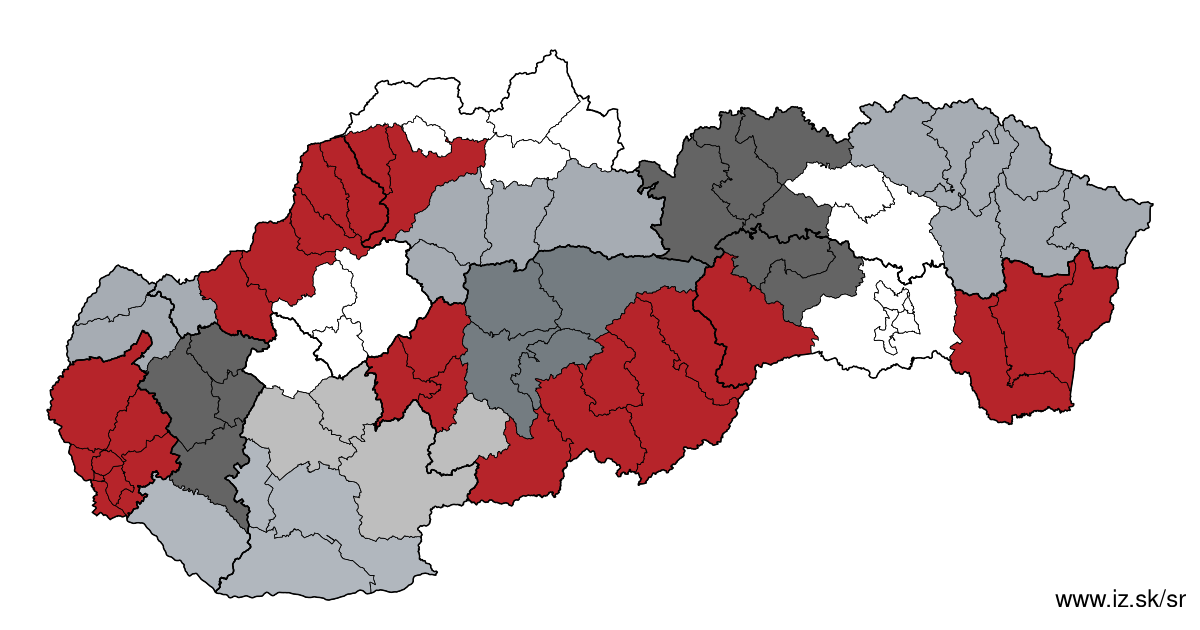
Regions of the Slovak Republic
Due to the need of analysis we have created regions of Slovakia. We will bring more information about these regions from the macroeconomic point of view as well as from the point of view of the labour market.. . .
Similar articles
Regions of the European Union, Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region, Local Administrative Units data of Visegrad countries, NUTS3 regions of Slovakia, Regions of the Slovak Republic, Labour market indicators of slovak regions., Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia, Counties of Slovakia


 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News